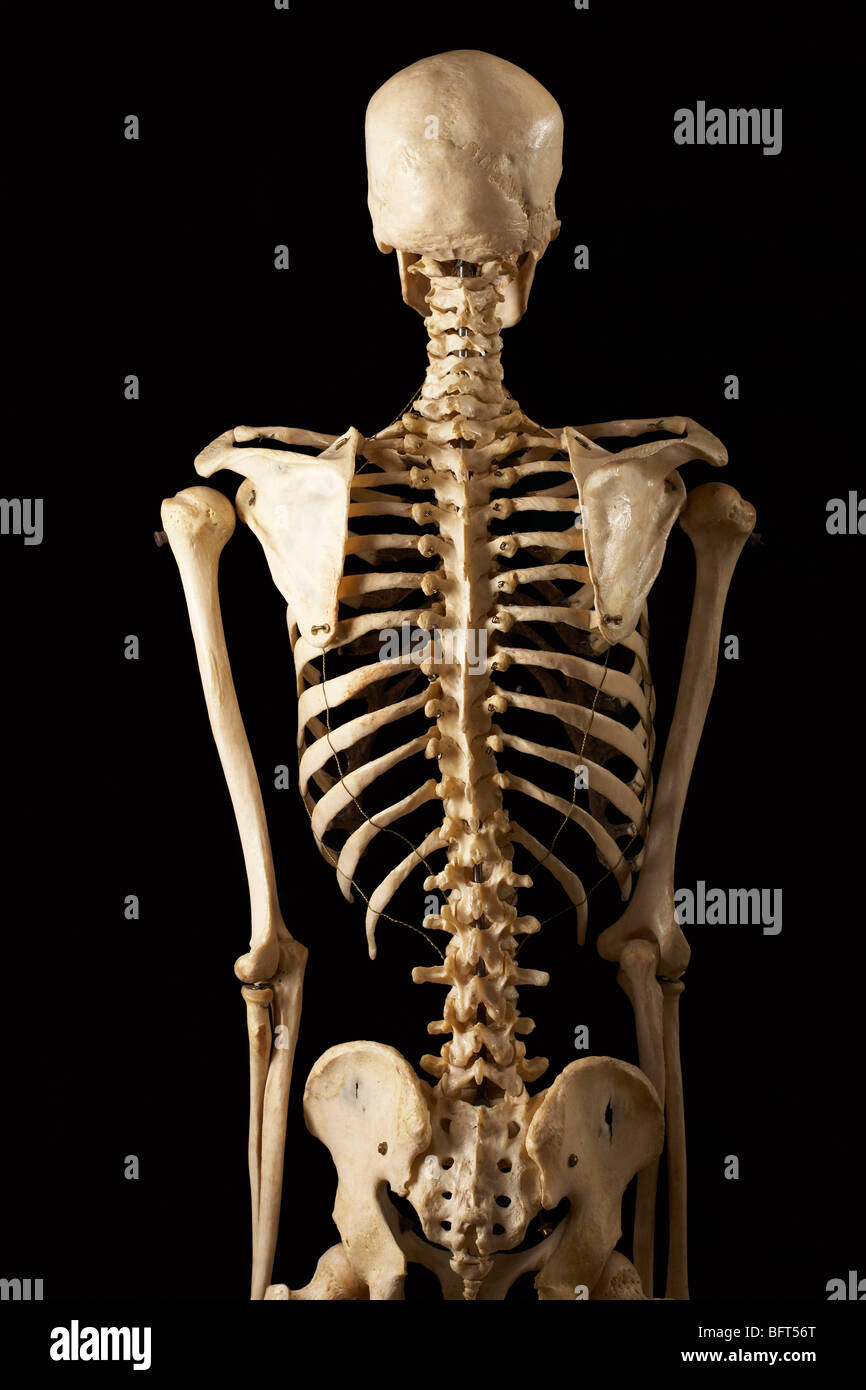
Posterior View of Skeleton Stock Photo Alamy
Create healthcare diagrams like this example called View of the Full Skeleton - Posterior in minutes with SmartDraw. SmartDraw includes 1000s of professional healthcare and anatomy chart templates that you can modify and make your own. 3/37 EXAMPLES. EDIT THIS EXAMPLE.

Anterior and Posterior view Human bones anatomy, Body bones, Skeleton
The vertebral column (spine or backbone) is a curved structure composed of bony vertebrae that are interconnected by cartilaginous intervertebral discs.It is part of the axial skeleton and extends from the base of the skull to the tip of the coccyx.The spinal cord runs through its center. The vertebral column is divided into five regions and consists of 33 vertebrae interlaced by strong joints.

Illustration of anterior and posterior views of human skeletal
Toggle Anatomy System. The bones of the pelvis and lower back work together to support the body's weight, anchor the abdominal and hip muscles, and protect the delicate vital organs of the vertebral and abdominopelvic cavities. The vertebral column of the lower back includes the five lumbar vertebrae, the sacrum, and the coccyx.
Posterior Anterior View
Finally, the skeleton grows throughout childhood and provides a framework for the rest of the body to grow along with it. Skeletal System Anatomy. The skeletal system in an adult body is made up of 206 individual bones. These bones are arranged into two major divisions: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton runs.

lateral human anatomy
3. The Skeleton Protects Vital Organs. The brain is surrounded by bones that form part of the skull. The heart and lungs are located within the thoracic cavity, and the vertebral column provides structure and protection for the spinal cord. 4. Interactions Between the Skeleton, Muscles, and Nerves Move the Body.
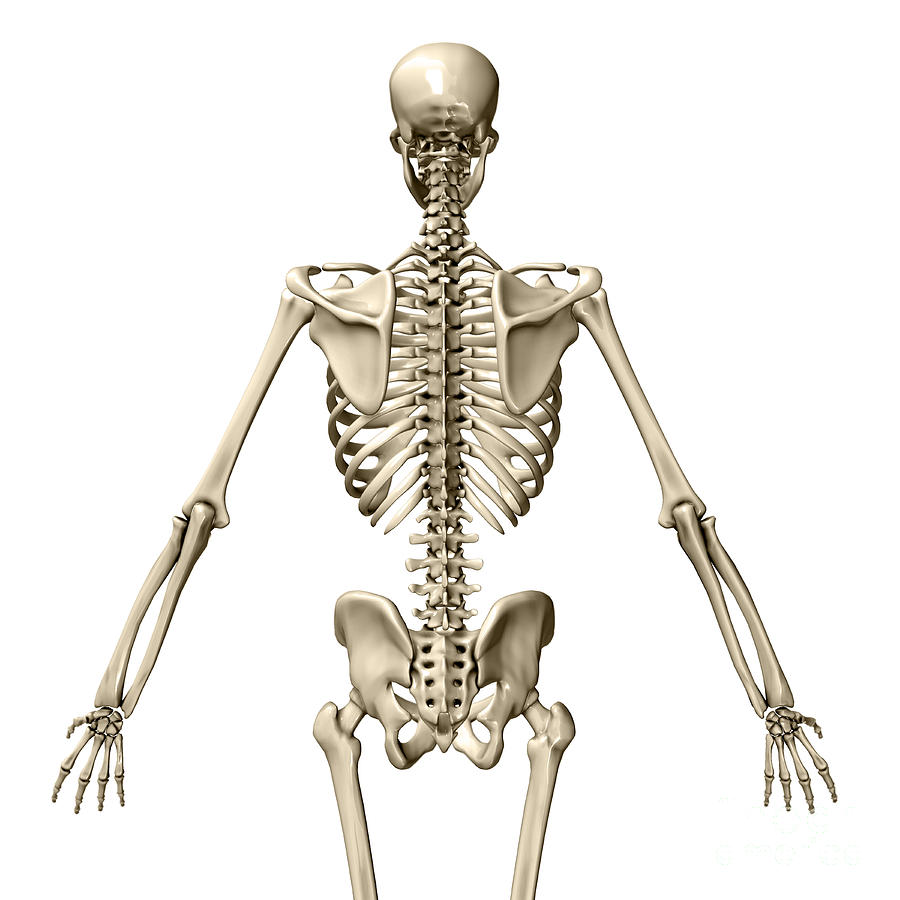
Human Skeleton, Posterior View Photograph by Evan Oto Fine Art America
parietal bone. Flat cranial bone articulating with the frontal, occipital, temporal and sphenoid bones; the two parietal bones form the largest portion of the dome of the skull. lateral view of skull.
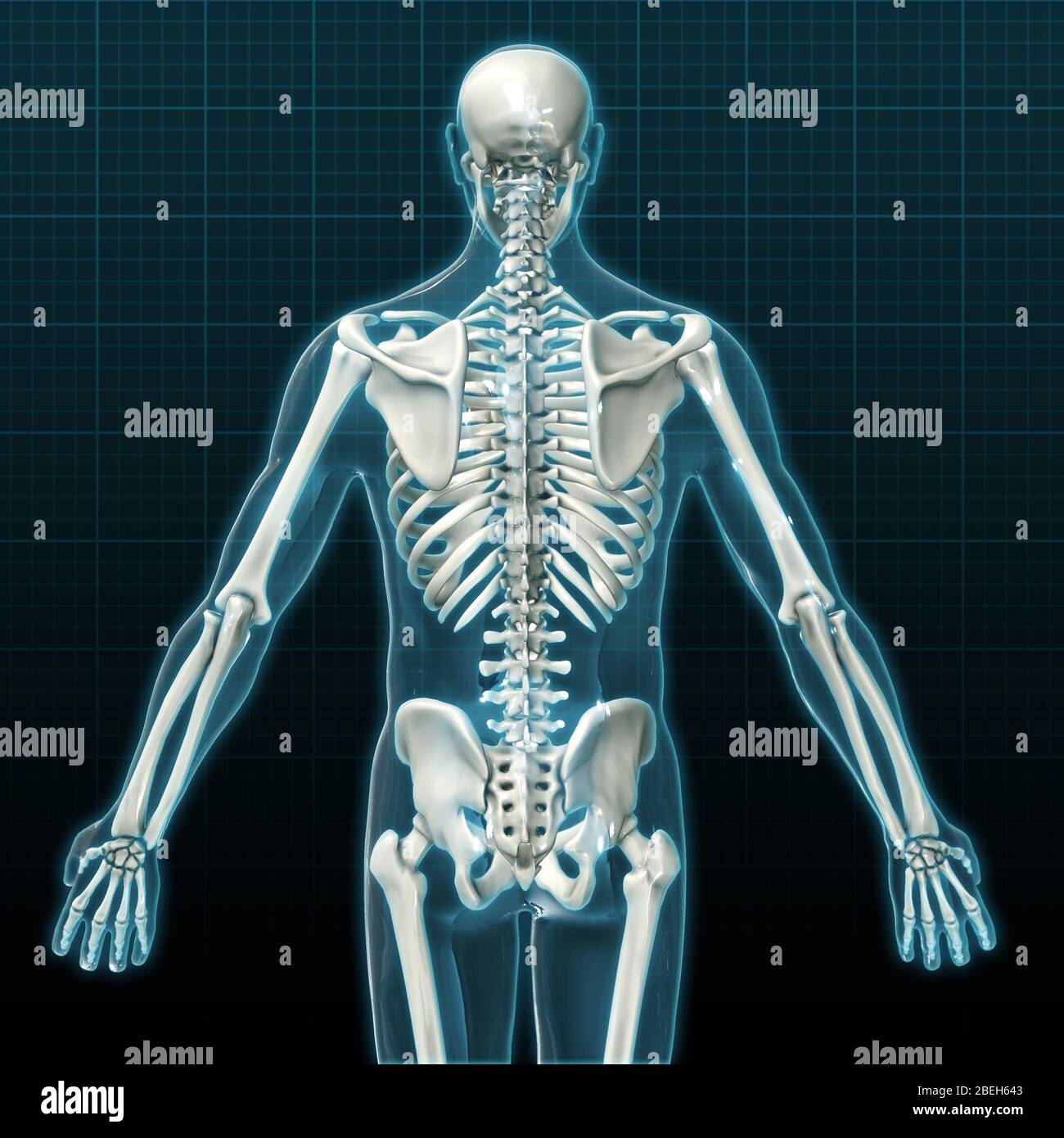
Human skeleton posterior view hires stock photography and images Alamy
6.1 Skeleton: Overview (See page(s) 84) Name at least five functions of the skeleton. Explain a classification of bones based on their shapes. Describe the anatomy of a long bone. Describe the growth and development of bones. Name and describe six types of fractures, and state the four steps in fracture repair. 6.2 Axial Skeleton (See page(s) 89)
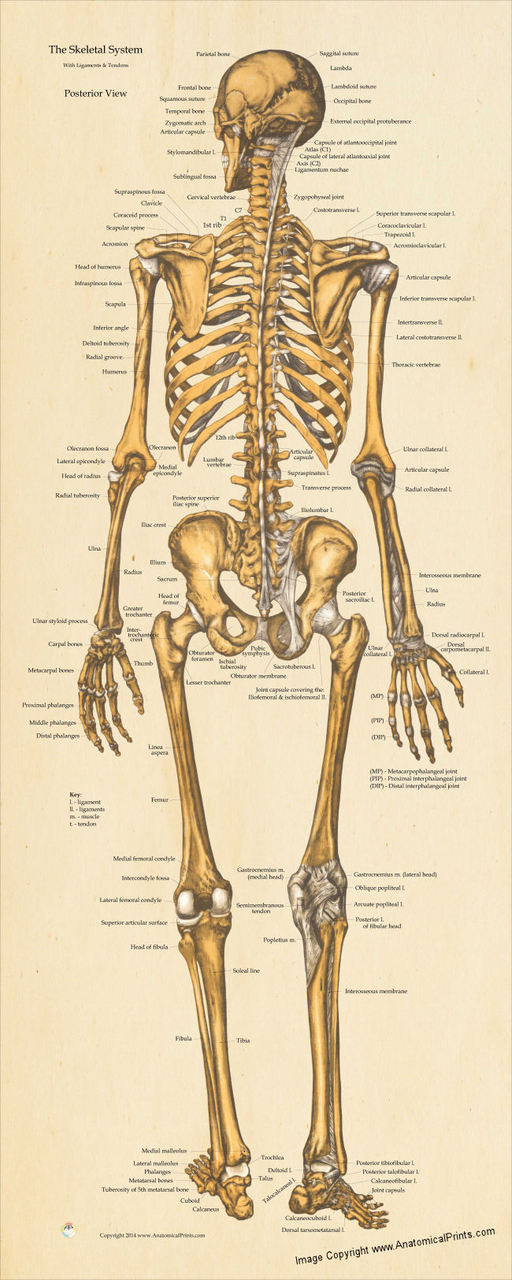
Skeletal System Posterior View Poster Clinical Charts and Supplies
creates a bridge-like structure that connects the temporal bone with the zygomatic bone forming part of the zygomatic arch. Above: Markings of the cranium with the following views: (A) anterior view, (B) lateral view of the left side of the skull, (C) posterior view, and (D) lateral view of the right side of the skull.
.PNG)
Skeletal System Presentation Biology
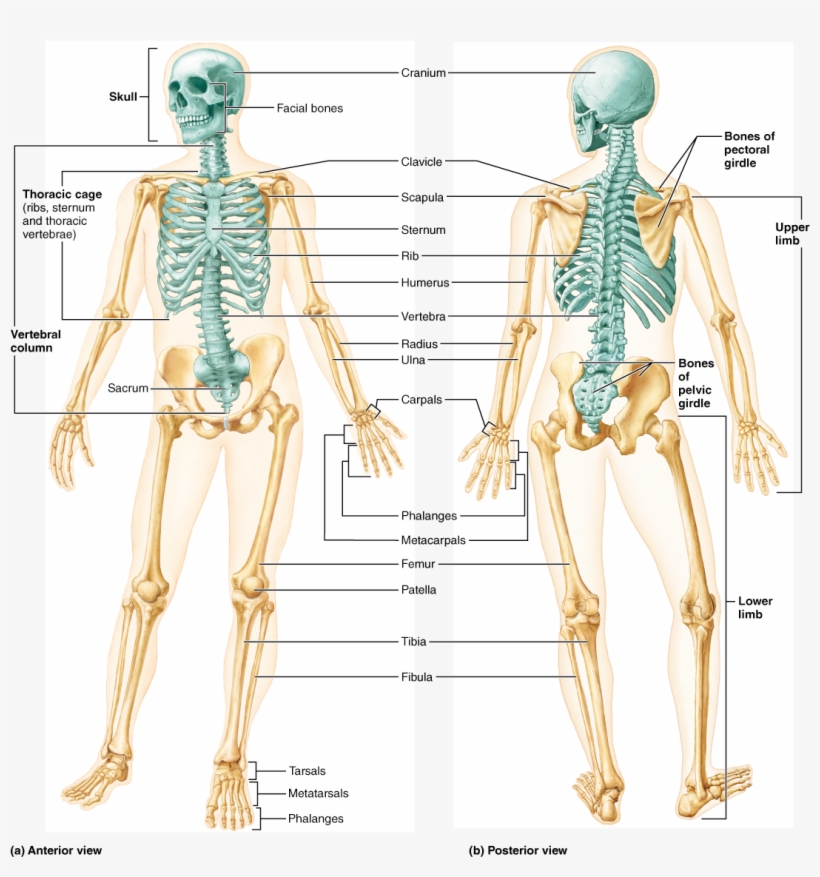
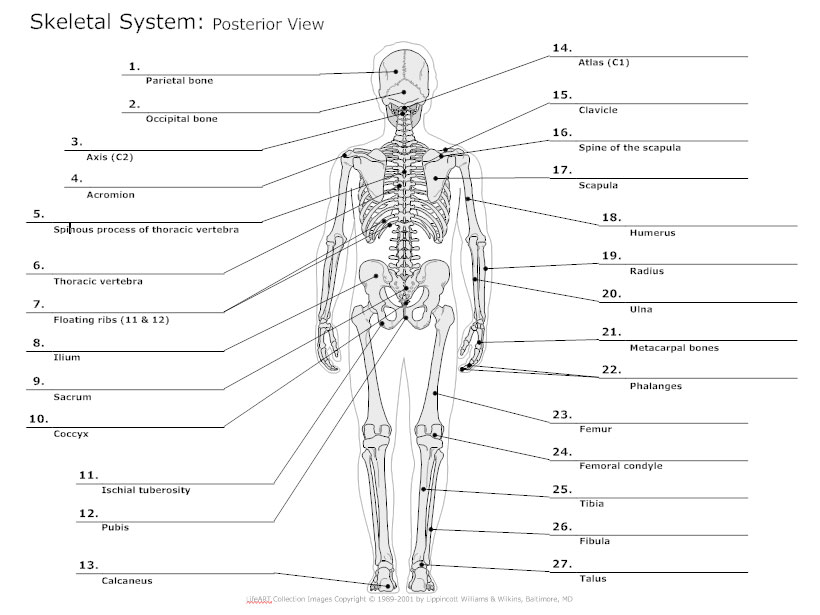
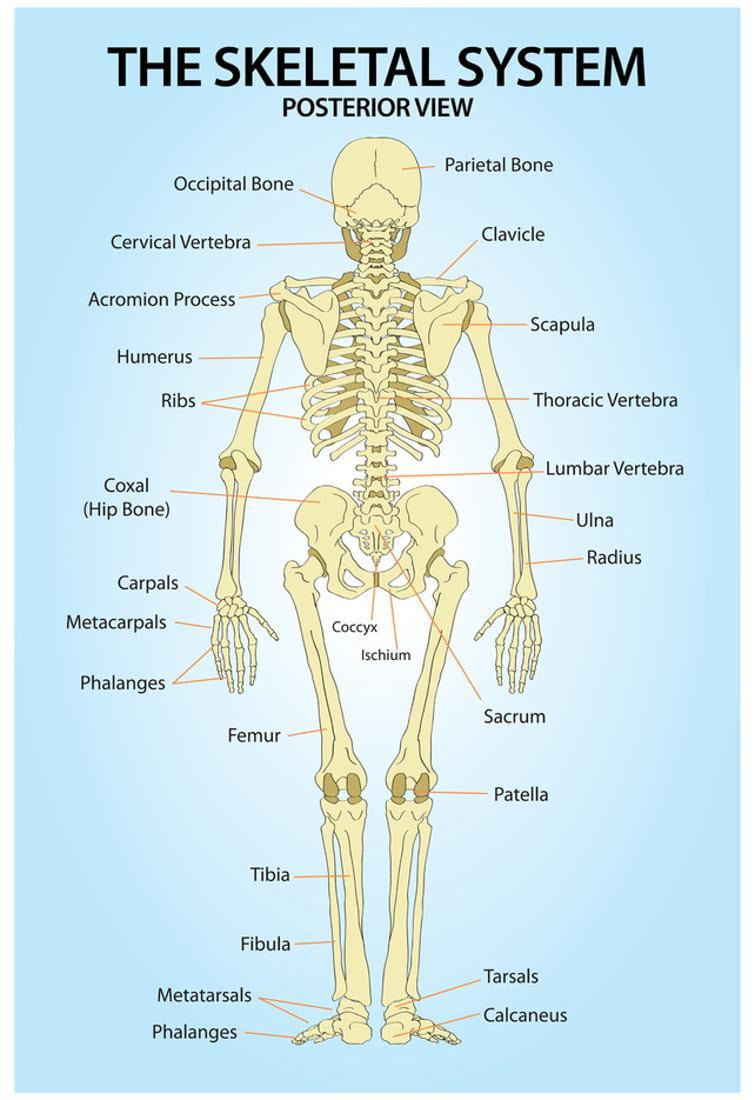
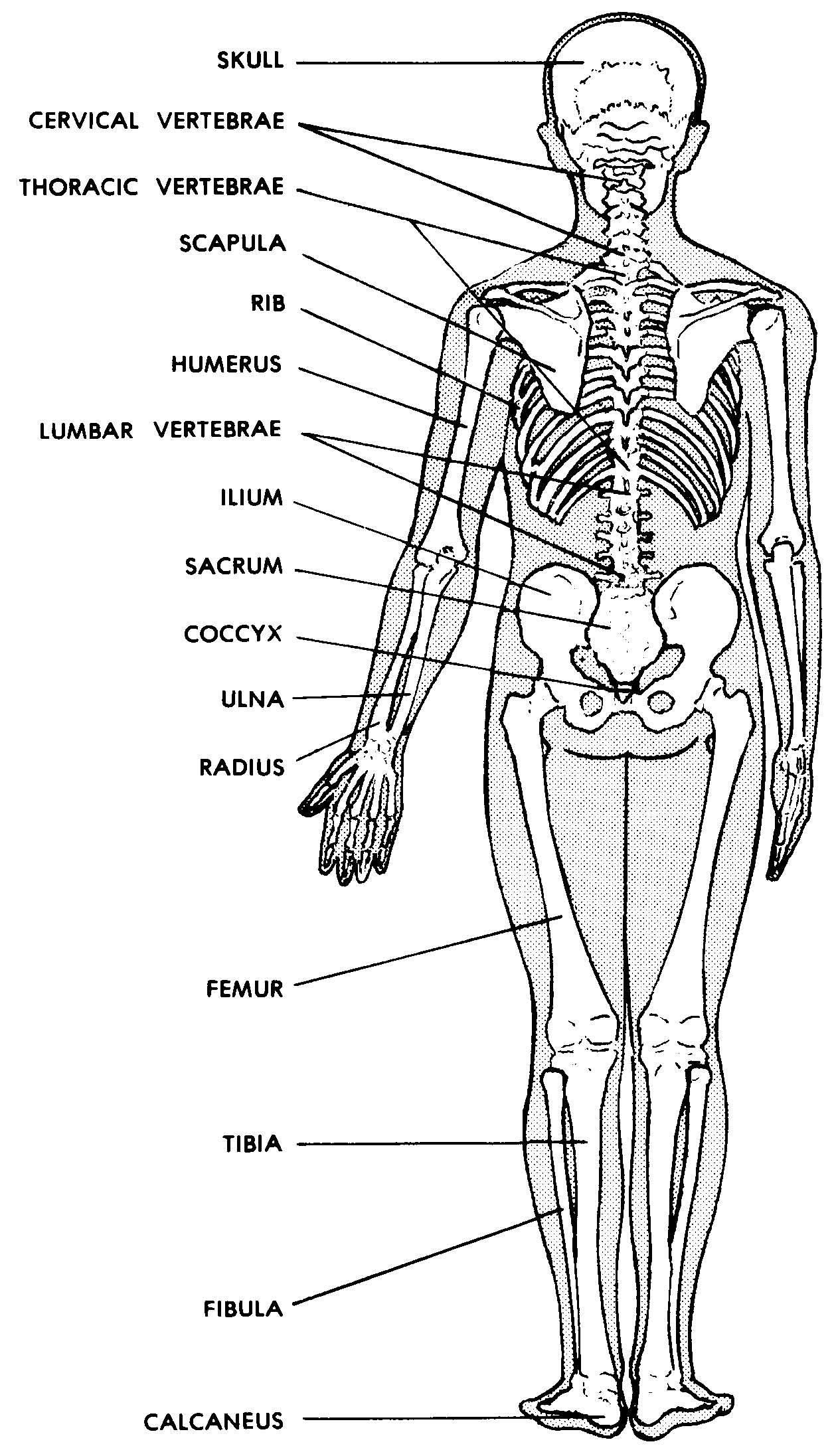
The posterior view of the skeleton reveals bones that are obscured in the anterior view, most notably, the entire stack of individual vertebrae that span vertically from the sacrum to the skull. The vertebrae are divided into three categories: those that form the neck (the cervical vertebrae), those to which the ribs are attached (the thoracic.
Bones, Part Human Skeleton Anterior And Posterior View PNG Image
The axial skeleton forms the vertical, central axis of the body and includes all bones of the head, neck, chest, and back (Figure 7.2). It serves to protect the brain, spinal cord, heart, and lungs. It also serves as the attachment site for muscles that move the head, neck, and back, and for muscles that act across the shoulder and hip joints.
Skeletal System Diagram Types of Skeletal System Diagrams, Examples, More
human skeleton, the internal skeleton that serves as a framework for the body. This framework consists of many individual bones and cartilages.There also are bands of fibrous connective tissue—the ligaments and the tendons—in intimate relationship with the parts of the skeleton. This article is concerned primarily with the gross structure and the function of the skeleton of the normal.
Skeletal System Posterior View Anatomy Print Poster 13x19
Figure 7.3.8 - Posterior View of Skull: This view of the posterior skull shows attachment sites for muscles and joints that support the skull. Sphenoid Bone. The sphenoid bone is a single, complex bone of the central skull (Figure 7.3.9). It serves as a "keystone" bone, because it joins with almost every other bone of the skull.

Human Skeleton From The Posterior View Didactic Board Of Anatomy Of
parietal bone. Flat cranial bone articulating with the frontal, occipital, temporal and sphenoid bones; the two parietal bones form the largest portion of the dome of the skull. lateral view of skull.

Vektor Stok Human Skeleton Posterior View Didactic Board (Tanpa Royalti
human muscle system, the muscles of the human body that work the skeletal system, that are under voluntary control, and that are concerned with movement, posture, and balance. Broadly considered, human muscle—like the muscles of all vertebrates—is often divided into striated muscle (or skeletal muscle), smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.Smooth muscle is under involuntary control and is.

skeleton posterior Real Bodywork
Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeleton—Anterior View Skeleton—Posterior View Bones of the Skull—Frontal View Bones of the Skull—Lateral View Types of Fractures Types of Traction Types of Synovial Joints For an in-depth study of the skeletal system, consult the following publications: Lewis SM, et al: Medical-surgical nursing, ed 8, St. Louis, 2011, Mosby.
Images 04. Skeletal System Basic Human Anatomy
Synonyms: none. This article will describe the anatomical structures which can be seen from a superior view of the skull base. This will include the various foramina, the nerves and arteries that pass through them, but also the structures of the brain and cerebellum, which all lie within the three main parts of the skull base called cranial.